In this article:
- The Importance of Teaching Physics in Early Years
- Teaching Physics Using Evidence and Research-Based Practices
- Activities to Teach Physics to Years F-6
- Storytelling’s Role in Teaching Physics
- How to Build a Curious Mindset through Physics Teaching
- Teaching Physics through Technology
- The Impact of Innovative Physics Teaching in Early Education
The Importance of Teaching Physics in Early Years
Introducing physics at an early stage serves as a cornerstone, laying a robust foundation for advanced learning in later years. By starting with concepts that might initially seem obvious or simple, such as movement, weight, size, shape and the basic principles of force (push and pull), along with fundamental ideas about heat, sound and energy, educators can spark a lifelong interest in the sciences.
These initial forays into physics are about teaching students about physics and fostering a sense of exploration and inquiry. When young learners engage with these elementary concepts, they are learning and at the same time developing critical thinking skills and nurturing their innate curiosity. This early exposure to physics encourages children to learn and observe, question and investigate their world, setting the stage for deeper scientific understanding and inquiry.
This approach, centred on learning, investigation and exploration, is crucial. It aligns with the innate learning processes of young children, who are naturally able to learn complex knowledge and be inclined to explore and understand the world around them. As educators, our role is to guide this exploration, turning every observation into a learning opportunity that is both engaging and foundational. Let’s delve into how we can effectively introduce these fundamental physics concepts to our young learners, fostering a love for science that will thrive throughout their educational journey.
This article will provide educators with practical and innovative strategies for teaching physics, aiming to make the subject more engaging and accessible for young students while aligning with modern scientific advancements.
Teaching Physics Using Evidence and Research-Based Practices
Effective physics education for young learners hinges on the incorporation of research and evidence-based teaching methods. Central to this approach is hands-on, project-based learning. These active learning strategies encourage students to engage directly with physical phenomena, fostering a deeper understanding of the concepts at play.
Explicit Direct Instruction plays a crucial role in grounding these experiences. By providing clear, concise explanations, rules and examples, educators can ensure that students grasp the fundamental concepts necessary to explore physics effectively. This foundational knowledge then sets the stage for a more student-led part of the learning process.
When students are present and confident in their learning journey, they are able to think more critically. They start to question, hypothesise and test their understanding in practical contexts. This shift from passive reception of information to active engagement in learning is pivotal. It leads to increased student engagement, as learners feel a greater sense of ownership and relevance in their educational experiences.
The success of this approach is evident in the increased curiosity and enthusiasm students show towards physics. By blending direct instruction with scientific enquiry and hands-on, student-led activities, educators can create a dynamic and interactive learning environment. This environment not only imparts knowledge but also instils a passion for learning and discovery, which is essential for the continued study of physics and other scientific disciplines.
Activities to Teach Physics to Years F-6
Engaging young minds in physics involves a mix of interactive activities and relatable content. Here are a few examples of activities that bring physics concepts to life:
- Exploring Movement through Play: Activities like kicking a ball, using a yo-yo, or playing with a slingshot can demonstrate the basics of force and motion.
- Investigating Shape and Movement: Using different objects like cubes, spheres or pyramids, students can observe how shape influences movement when rolled down slopes.
- Understanding Weight and Movement: By pushing objects of different weights, like heavy and light cubes or spheres, students can see how weight affects speed and distance.
- Size and Movement: Comparing the movement of large and small objects, like beach balls or toy cars, helps students understand the impact of size on movement.
Each of these activities is designed to make physics concepts tangible and engaging for young learners. For a more detailed breakdown of useful activities by year, don’t forget to explore our comprehensive article on activities for teaching physics (coming soon!). This resource offers tailored activities for each year from Foundation to Year 6 to help you bring physics to life in your classroom.
Storytelling’s Role in Teaching Physics
Beyond activities, engaging students in physics requires a blend of creativity and practicality. A particularly effective strategy is the use of storytelling to discuss physics concepts and inventions. This approach not only makes the subject more relatable but also tailors it to their age group, making complex ideas accessible and exciting.
Incorporating elements from their daily lives in these stories helps bridge the gap between theoretical physics and the real world. It allows students to see the relevance of what they are learning, fostering a deeper connection with the subject. Additionally, activating prior knowledge through storytelling aids in the retention of new concepts, as students can build on what they already know.
The use of visual aids like videos, images and simple diagrams plays a significant role in this storytelling approach. These tools not only enhance understanding but also cater to different learning styles, ensuring that all students can grasp the concepts being taught.
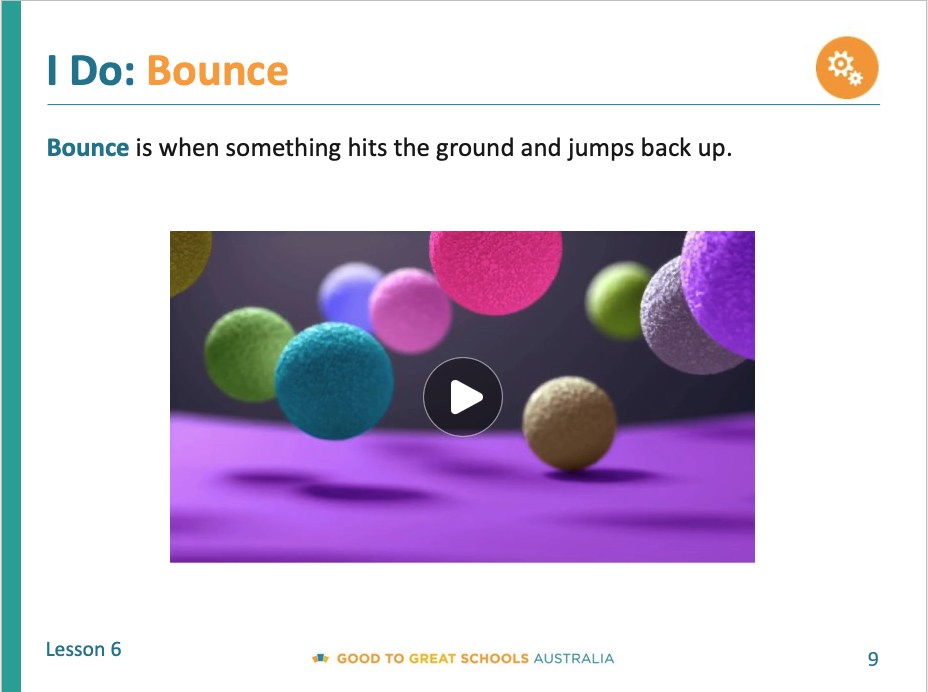
Example of video used in the GGSA Physics Curriculum to illustrate the contept of bounce.
Example of video-based activity for teaching the concept of sound pitch.
Discover the full range of teaching resources available in our newly updated GGSA Physics Curriculum for Foundation to Year 3.
By combining these various elements, physics becomes more than just a subject; it turns into a series of engaging stories and experiences that students can relate to and understand, making their learning journey both enjoyable and effective.
How to Build a Curious Mindset through Physics Teaching
Fostering a curious mindset in young learners is pivotal in teaching physics effectively. This involves nurturing their inquisitiveness and problem-solving skills. Rather than simply talking students through concepts, educators should encourage exploration and questioning. This can be achieved by:
- Engaging Students with Questions: Instead of lecturing, teachers should frequently pose questions to students, prompting them to think and explore physics concepts critically.
- Encouraging Student Queries: Create an environment where students feel comfortable and encouraged to ask their own questions. This not only enhances their understanding but also promotes a culture of curiosity and inquiry.
By adopting these approaches, educators can transform physics lessons into interactive and thought-provoking sessions, cultivating a generation of curious and engaged young minds.
Teaching Physics through Technology
The integration of technology in physics education is a crucial step towards blending traditional teaching methods with the digital age. Utilising digital tools and online resources offers innovative ways to explore physics concepts:
- Digital Tools for Practical Learning: For example, students can use apps to measure decibels in different areas of the school, providing a hands-on approach to understanding sound and its properties.
- Interactive Learning through Apps: Apps can also be used to explore complex concepts like soundwaves, making abstract ideas more tangible and understandable.
Here are just some of the applications used throughout the GGSA Physics Curriculum to teach important concepts such as sound and sound waves:
- Sound meter app: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.splendapps.decibel&hl=en&gl=US or https://apps.apple.com/us/app/decibel-x-db-sound-level-meter/id448155923
- Sound waves measuring app: https://musiclab.chromeexperiments.com/Sound-Waves/

How the GGSA Physics Curiculum incorporates technology such as apps into teaching.
While technology is essential for preparing students for a digital future, the benefits of offline learning are still significant. A balanced approach that combines traditional teaching methods with modern technology helps students not only grasp physics concepts but also become adept at using technology. This approach ensures students are well-equipped for the future of work and study.
Assessment and Feedback when Teaching Physics
Effective assessment techniques are key in evaluating physics learning. Quick, end of lesson quizzes can serve as a rapid check for understanding, allowing teachers to gauge students’ grasp of concepts in real-time. Additionally, observation and targeted questioning during activities can provide insights into students’ comprehension and engagement.
For final assessments, simplicity is crucial. These should focus more on gauging engagement and understanding rather than rote memorisation. Constructive feedback, integral to this process, should aim to enhance understanding and guide students towards deeper exploration of physics concepts. This approach ensures assessments are not just a grading tool but a part of the learning journey, fostering continuous improvement and curiosity.

Example of interactive quiz testing students’ understanding of sound pitch.
The Impact of Effective Teaching in Early Physics Education
Innovative teaching methods play a pivotal role in laying a strong foundation in physics for young learners. These methods not only build foundational science knowledge but also significantly enhance student engagement. Starting as early as possible with these engaging approaches allows students to grasp the main physics concepts effectively. This early start is crucial in shaping their understanding and appreciation of physics, setting the stage for a lifelong interest and proficiency in the sciences.
If you’re interested in more ready-to-teach resources for teaching physics to primary school students, explore our recently updated physics curriculum. You can sign up and start using 100s of classroom, professional learning and school improvement resources completely for free today. Just click the button below and start your journey towards mastery teaching!



